

As we all know, Sustainable development involves a development strategy that balances current necessities with the preservation of future generations’ capacity to fulfil their own needs. It encompasses three pillars of sustainability and strives to tackle diverse social, environmental and economic challenges to advance the cause of sustainable development. Sustainability is a multi-dimensional and critical parameter towards the existence or extinction of all.
Achieving this objective requires a collaborative effort, which was foreseen through the adoption of the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The endorsement of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs) in 2015 represents a set of ambitious targets aimed at eradicating poverty, conserving the
environment, and enhancing the well-being of all.
Each of these 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is linked to a set of 169 corresponding targets and supported by 244 official indicators. These indicators play a crucial role in gauging progress towards the attainment of the SDGs, providing a means for countries to assess their advancement and make informed choices in the realm of sustainable development.
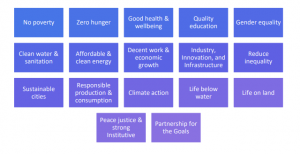
Needless to say, all SDGs are interrelated and interdependent and are paving ways towards sustainable planet. In today’s world, sustainable business is a Critical parameter and almost all business faces issues relating to their environmental concerns, social & ethical engagements, governance & operational practices, and financial impact. These impacts can be actual or potential, negative, or positive, long term or short term, intended or unintended, reversible, or irreversible, local, or global and indicates the company’s impact on Sustainability. Based on these impacts, companies need to identify the material topics that represent their most significant impact and should choose their appropriate need-based social and environmental activities to be undertaken by companies and allocate adequate resources including manpower, budget accordingly for such social and environmental activities. Various Social and Environmental Initiatives are slowly and steadily transforming countries and pushing all Nations toward the achievement of sustainable development goals and sustainability.
The achievement of such objectives, however, is facing a lot of failures and challenges primarily due to poor-quality data, non-availability of appropriate reporting, lack of impact monitoring, lack of auditing framework. Credible social and environmental engagement framework is the key to achievement of Sustainable Goals. Such framework can provide methodology to select social and environmental projects, implementation and integration of such projects and their impact evaluation methodology. Companies need to realize that apart from their actions to demonstrate compliance with the law, it is imperative to report the effective use of the money spent on developmental activities in the form of impact accrued or created per rupee spent, primarily with the targeted
beneficiaries, by adopting a structured and uniform approach towards implementing social or environmental activities.
A robust and credible Sustainability framework across the countries to assess its such data, investigating the gaps, identifying the mitigative measures, and taking actions to plug them and integrate them into business operations is the need of hour which can lead to informed decision-making and can contribute immensely to the achievement of Sustainability.
Undoubtedly, SDGs reporting has become an integral component of companies’disclosure requirements. In this Initiatives, Indian government, and SEBI, the regulatory body has mandated sustainability performance reporting for top-listed companies. Nevertheless, attaining the Sustainable Development Goals presents a formidable and
intricate undertaking, characterized by its challenges of extensive, tangible/ intangible data and time-consuming nature. The absence of a well-defined strategy and a standardized framework for tracking key performance indicators has impeded the transformation of SDG commitments into tangible business initiatives. Implementing a unified social and environmental guidance framework for sector specific sustainability disclosures relevant to the companies can prove to be a milestone.
Implementing IS/ISO 26000 Guidance on Social Responsibility: Unified Framework
IS/ ISO 26000 Guidance on Social Responsibility was formulated in 2010 to help organizations effectively assess and address social responsibilities that are relevant and significant to their mission and vision. IS/ISO 26000 aimed to provide guidance to organizations on how to integrate social responsibility into their operations and decision making processes.
Since, IS/ISO 26000 and the SDGs both promote sustainable and socially responsible practices, IS/ISO 26000 can be used by organizations as a coherent framework to align their activities with the broader objectives of achieving SDGs.
What is IS/ISO 26000 Guidance on Social Responsibility?
The objective of IS/ISO 26000 is to support organizations in addressing their social
responsibilities while taking into account cultural, societal, economic, environmental, and legal diversities. It also seeks to enhance awareness regarding the concept of social responsibility.
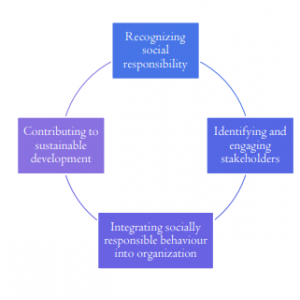
Social Responsibility: Principles
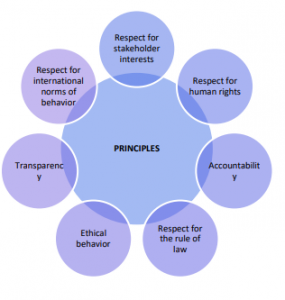
As per IS/ISO 26000, to maximize contribution to sustainable development, while practising social responsibility, the organization are advised to adhere Seven Key Underlying Principles of Social Responsibility.
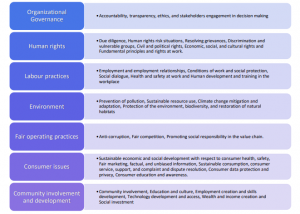
What are the issues involved in Core Subjects?
Social Responsibility throughout an Organization: Integration
Integrating social responsibility is putting social responsibility into practice on existing systems, policies, structures, and networks of the organization. Organizations may establish techniques for introducing new approaches into their decision making and activities, as well as effective systems for communication and internal review to integrate social responsibility into the way organisations operates and contribute to sustainable development.
Social Responsibility Reporting
IS/ISO 26000 Guidance on social responsibility guides that, at appropriate intervals, organisations should report on their performance on social responsibility to the stakeholders. The standard suggests that Social Responsibility Reporting should include:
─ Information about organisations objectives and performance on the identified core subjects and relevant issues of social responsibility
─ How and when stakeholders have been involved in the identifying core subjects
─ How well the social responsibility is integrated in its organisation activities.
─ A fair and complete picture of performance, including achievements and shortfalls, and the way in which shortfalls will be addressed in future.
IS/ ISO 26000 is an overarching framework for Social Responsibility (SR) and is used by many companies as a way of strategizing and managing their SR performance. IS/ ISO 26000 offers practical guidance to any organization, anywhere in the world, wishing to contribute to sustainable development.
How users of IS/ISO 26000 contribute to the sustainable development goals (SDG)
IS/ISO 26000: 2010 was developed before the UN 2030 Agenda yet IS/ISO 26000 offers more than 400 recommendations related to its main principles and core subjects of social responsibility that help organizations contribute to the SDG goals.
As the core subjects mentioned in IS/ISO 26000 are in alignment with SDGs, an organization that acts according to the practical recommendations offered in IS/ISO 26000 will very well contribute to achieving specific SDGs related to social responsibility, human rights, labour practices, environment, and other relevant areas.
For further details on IS/ISO 26000 – Guidance on Social Responsibility, you may refer the Standard. IS/ISO 26000: 2010 is available for online purchase via www.standardsbis.in.
Mrs Shalu Varshney
Sc D | Joint Director, Bureau of Indian Standards