Indian Standards On Smart Cities – Triggering Standards-based Technology Adoption In Smart Cities
The Government of India started its smart cities mission in June 2015 to develop 100 Smart Cities across the country with an objective to provide a decent quality of life to its citizens using smart solutions. The mission focuses on harnessing technology, especially technology that leads to Smart outcomes and the creation of cities that are properly connected, adaptive, efficient, and resilient.

Standards based technology adoption in Smart Cities can create a level playing field for a diverse set of solution providers to offer world-class products and technologies, at the most affordable prices. This approach also helps Indian Smart Cities to become the lighthouses to guide other cities around the world and helps the companies, system/solution providers to become globally competitive.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has embraced the vision of Smart Cities and has embarked on an ambitious journey to develop a comprehensive set of standards for Smart cities, covering all aspects of the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), pertaining to Smart Cities. These include an overall master document, the ICT Reference architecture, followed by a host of standards to cover, Data and associated technologies, Geographical Information Systems (GIS), Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, Communication protocols, E-governance Systems and Data models and Taxonomy standards for all the relevant domains for Smart Cities.
So far BIS, with the help of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, and other stakeholders such as system integrators, vendors, solution providers has published 10 indigenous standards under one of its technical committees, namely, “Smart Infrastructure Sectional Committee LITD 28”. Four of these standards were published in December 2020 and six standards were published very recently in June 2021. These standards will not be static entities but will continually evolve as per the learnings from actual practice and evolving needs.
Standards published so far…
- 1. IS 18000:2020 Unified Digital Infrastructure – ICT Reference Architecture (UDI-ICTRA)
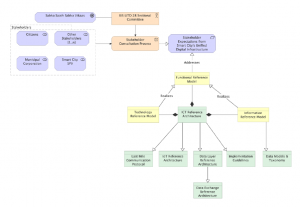
This standard defines the reference architecture and models for information and communication technologies needed to realize a Unified Digital Infrastructure (UDI) in Smart Cities. The reference architecture includes functional reference models, technology reference models and information reference models. The standard offers a blueprint for realizing the unified digital infrastructure but does not mandate any specific components. The reference architecture can be used to define various levels of architectural maturity, based on which components are included, from a basic level to an advanced level of the unified digital infrastructure.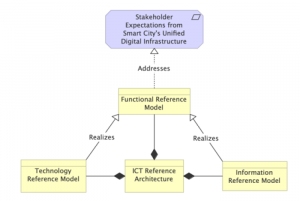
- 2. IS 18002 (Part 1):2021 Unified Digital Infrastructure — Data Layer Part 1 Reference Architecture
This Standard describes the data layer reference architecture that comprises the key data principles that every smart city sub-system needs to adhere to, the core capabilities required to be implemented at the city level for realizing the data layer, the functional reference model, the technology reference model, and information reference model.
The Data Layer Reference Architecture is intended to be used by stakeholders such as Smart city Data Officers, Smart City CEO’s, Policy and Governance officers, Auditors and other stakeholders involved in smart city implementation to define the city’s data architecture goals and to roll out solutions adhering to the defined goals.
- 3. IS 18003 (Part 1):2020 Unified Data Exchange Part 1 Architecture.
This Standard describes the architecture for the data exchange, interfaces of data exchange components and the use cases that are enabled in the ecosystem. It also describes the responsibilities of various stakeholders, their interactions with other stakeholders in the system, and the respective consequences of those interactions.
This Standard also describes the high-level architecture of the following three main components of the data exchange services:
a. Catalogue service that provides APIs to manage meta-information about resources.
b. Authorization service, that manages authorization to access the resources; and
c. Resource access service, that provides a standardized way to access resources
- 4. IS 18003 (Part 2):2021 Unified Data Exchange Part 2 API Specifications
This Standard defines Unified Data Exchange interface specifications. It defines a set of APIs that enables controlled and secure any-to-any exchange of all forms of public and privately owned non-personal data between data providers and consumers. The API specifications are defined for usage over HTTP protocol only.
The standardized APIs defined in this standard help build robust application ecosystems that not only improve development cycle times but also lead to improvement in reusability and extensibility of the developed applications.
- 5. IS 18004 (Part 1):2021 IoT System Part 1 Reference Architecture
This Indian Standard describes the Internet of Things (IoT) Reference Architecture, that comprises IoT Concept Model, IoT Reference Models (Domain based IoT reference model, Entity based IoT reference model) and IoT Deployment Views.
IoT Concept Model and Reference models elaborate the interactions between various entities, both digital and non-digital.
The Standard is useful for anyone involved in the design, development, deployment, and implementation or certification of an IoT device, network, or application ecosystem. This standard can serve as a template for both the city administrators and those who are the consumers of such IoT, and ICT based solutions, as well as the IoT and ICT solution providers who develop and deploy such solutions.
- 6. IS 18006 (Part 1):2021 Municipal Governance Part 1 Reference Architecture
This Indian standard defines the reference architecture and models for Municipal Governance in Urban Local Bodies (ULBs). The reference architecture includes business reference model, technology reference model and information reference model.
This standard addresses stakeholders’ expectations for efficient municipal operations as well as to enable equitable service delivery to citizens. The cities or municipal corporations can also use this standard as a guide to compare their current initiatives and functionalities.
- 7. IS 18006 (Part 3/Sec 1):2021 Municipal Governance Part 3 Property Tax Section 1 Taxonomy
This Indian standard provides a unified view of the Property Tax in a municipal corporation and introduces common and widely accepted terminologies and definitions that can be used across multiple systems.
The standard will help review and categorize Municipal Governance Property Tax, to map and define common processes, stakeholders, and reports. This standard can be used to analyze current city domain models, processes and reports & KPIs. Property Tax Taxonomy will also be used in developing Data Models and API Definitions as well as for creating metadata specifications. Together these standards will ensure semantic and syntactic interoperability among e-Governance systems in India.
- 8. IS 18008 (Part 1):2021 Smart Cities — GIS Part 1 Reference Architecture
This Indian standard describes the Enterprise GIS reference architecture that comprises the functional architecture, technical reference model, and information reference model of the enterprise GIS. It will provide a conceptual GIS architecture, application use cases and functionalities for spatial decision making. Functional requirements are provided to guide the cities in usability of the GIS. The use cases will guide the city in understanding the GIS applicability in a standardized way.
- 9. IS 18010 (Part 1):2020 Unified Digital Infrastructure – Unified Last Mile Communication Protocols Stack Part 1 Reference Architecture.
The standard provides a reference architecture on how different communication technologies can be harmonized to coexist at lower layers of the communication stack, while keeping unified upper layers (Application and Data Semantics) running over different communication technologies.
- 10. IS 18010 (Part 5/Sec 1):2020 Unified Digital Infrastructure – Unified Last Mile Communication Protocols Stack – Part 5 Network Access Layer (IEEE 802.15.4) Section 1 Specification.
The standard describes the Physical Layer and MAC layer specification based on IEEE 802.15.4 using Sub-Giga Hz spectrum 865 – 867MHz. Adoption of this standard will ensure device level interoperability between different vendors using IEEE 802.15.4 using 865-867MHz spectrum.
Standards on the horizon…
After these broader framework standards, the committee, LITD 28 will be developing the next set of standards that will help the stakeholders in the implementation of the Reference architectures described in the aforementioned standards. The committee is also setting a roadmap for developing more detailed granular standards for specific implementation aspects.
BIS has also submitted a few of these to international standardization bodies for consideration to become global standards.
Together these standards will ensure a harmonized, secure, and sustainable Digital infrastructure to facilitate interoperability between systems, processes and platforms in the diverse multi-vendor, multi-network and multi-service environment that exists in the smart cities. These standards will also help in bringing down the cost of implementation of the Smart City projects to a great extent.
Written by – Manikandan K
Scientist-D | Electronics and IT Department
Bureau of Indian Standards
Go Back




