
भारतीय मानक ब्यूरो के द्वारा सूचना और प्रलेखन — पुस्तकालयों में आरएफआईडी – भाग 1 कार्यान्वयन के लिए डेटा एलिमेंट्स और सामान्य दिशानिर्देश, सूचना और प्रलेखन — पुस्तकालयों में आरएफआईडी – भाग 2 आईएसओ/ आईईसी 15962 के नियमों पर आधारित आरएफआईडी डेटा तत्वों की इनकोडिंग और सूचना और प्रलेखन — पुस्तकालयों में आरएफआईडी – भाग 3 निश्चित लंबाई इनकोडिंग भारतीय मानको का प्रकाशन किया गया है |
Bureau of Indian Standards published new Indian standards pertaining to Information and Documentation namely IS 16602: 2018 / ISO 28560-1: 2014 Information and Documentation – RFID in libraries — Part 1: Data elements and general guidelines for implementation, IS 16602- 2 : 2017/ ISO 28560 -2 : 2011 Information and Documentation RFID in Libraries Part -2 – Encoding of RFID Data Elements Based on Rules from ISO/IEC -15962 and IS 16602-3 : 2017 /ISO – 28560 -3 : 2014 Information and Documentation RFID in Libraries – Part 3 fixed length Encoding.
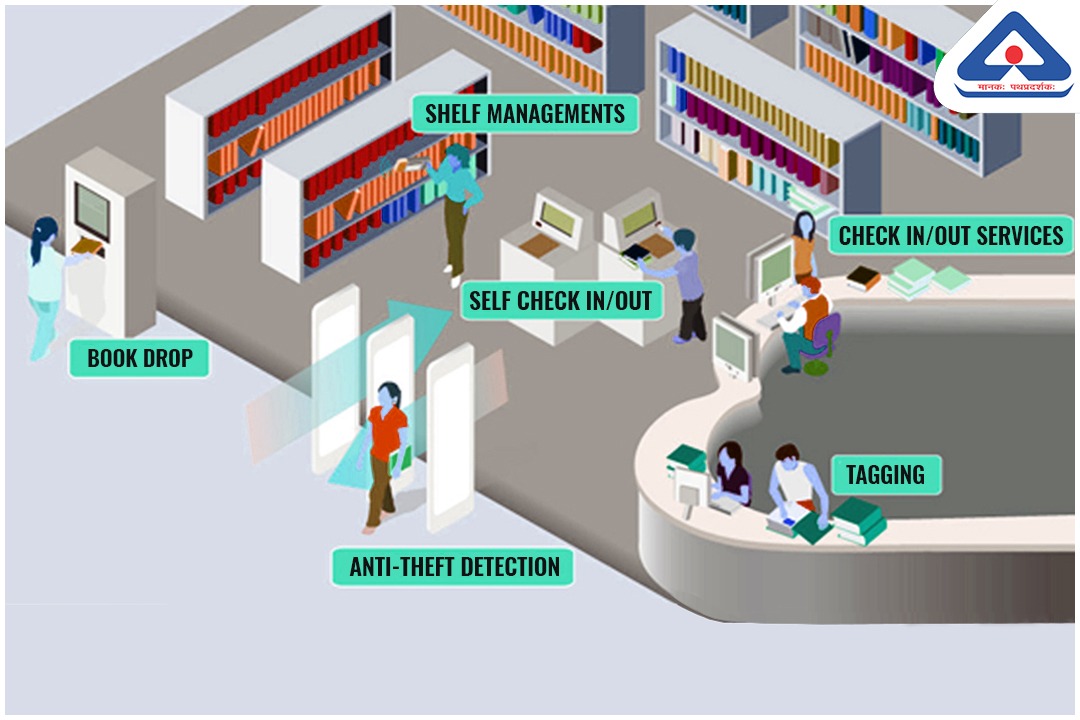
In order to keep pace with the latest technological developments in the field of Information and documentation, Management Systems Department has recently adopted International Standard IS 16602(Part 1):2018 / ISO 28560-1:2014 on RFID in libraries -Part 1: Data elements and general guidelines for implementation, which specifies guidelines for the use of radio frequency identification (RFID) tags for the needs of all types of libraries by defining various data elements used in libraries such as Unique identification No, owner, publisher, printer, author, ISBN, Year, borrower, shelf location, etc.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is the latest technology to be used in the library that combines security with more efficient tracking of materials throughout the library, including easier and faster processing, inventorying, and materials handling.
IS 16602 (Part 1):2018 / ISO 28560-1:2014 provides the framework to RFID-based systems that can be implemented for easier / faster tracking of documents throughout the libraries along with the security of materials, inventorying, stock verification, shelf handling and ensuring interoperability between libraries to exchange library items with RFID tags.
RFID is a combination of radio-frequency and microchip. RFID uses wireless radio communications to uniquely identify objects and is one of the fastest-growing automatic data collection (ADC) technologies, which is comprising one or more readers and RF transponders/ chip in which data transfer is achieved by means of suitable radiating electromagnetic carriers/ tag. When these tags pass through a Radio Field generated by a reader, the transponder in the tag transmits the stored information back to the reader, thereby identifying the object.
The information contained on microchips in the tags affixed to library materials is read using radio frequency technology regardless of item orientation or alignment and distance.
The important feature of power supply to the transponder is drawn either from the field of the reader (Passive tag) or from the battery incorporated in the tag (Active/Semi-active tag).
The use of RFID reduces the amount of time required to perform circulation operations. The most significant time savings are attributable to the fact that information can be read from RFID tags much faster than from bar codes and that several items in a stack can be read at the same time without tipping them out or removing them.
RFID library systems claim an almost 100 percent detection rate using RFID tags. Using this wireless technology, it is possible not only to update the inventory but also to identify items that are out of proper order.
RFID tags last longer than barcodes because nothing comes into contact with them. Most RFID vendors claim a minimum of 100,000 transactions before a tag may need to be replaced.
Developments in RFID technology continue to yield larger memory capacities, wider reading ranges, and faster processing. RFID can be a solution to enhance further the automation and tracking of documents at an increased pace, with more libraries joining the trails. RFID is increasing in popularity among libraries, as the early adopters of this technology have shown that, it makes good economic sense, both for large and small libraries.
These standards are available for purchase at various BIS sales outlets and may also be purchased online at the link www.standardsbis.in.
Written by:-

Mrs. Shalu Varshney
Scientist C (MSD)